Your website is your ambassador to potential clients, employees, and experts. Your website should be optimized to reach as many interested people as possible and to keep their interest once they are on your website. This optimization process should be consistent and gradual. You may have to improve your website’s structure, navigation systems, internal and external links, and load performance to ensure your website is running as optimal as possible.
To help you optimize your law firm’s website, here is a detailed overview for on-page SEO optimization.
Why Law Firms Need On-Page SEO Optimization
The primary job of a law firm website is to market your practice. If your website isn’t bringing in new prospective clients, you may need to redesign it so that it will. On-page SEO optimization, also known as Onsite SEO or Technical SEO, is the tool to accomplish this.
Technical SEO applies to organic local rankings as much as it does general (non-local) rankings. Factors for search engine optimization include crawlability and understanding. Crawlability refers to a search engine’s ability to crawl through your website and mimic a navigational click-path for a user to take. Understanding occurs when a search engine is able to understand what a website is about.
The Do’s and Don’ts of On-Page SEO
On-page SEO Optimization is about maintaining your website in a consistent and user-free manner. The “Dos” of On-Page are about ensuring that your website runs consistently and error-free. Below are common SEO practices you should utilize when running your website and SEO efforts:
Do:
- Use Standard SEO Best Practices – You should use standard SEO best practices to obtain best results: conduct keyword research, organize your website, set up backlinks (or backlink magnets), and focus your website on local SEO areas.
- Be Consistent – Consistency is a large part of SEO. The search engine needs to know you’re not “gaming” the system and that your website is an authentic source.
- Be Patient – SEO should be done methodically. Results will not be instantaneous and quick. Also, don’t overreact or overcorrect, particularly to rapid, short-term fluctuations in a keyword SERP.
You should also avoid certain practices to maintain the best SEO optimization for your webpage. One of the most important “Don’ts” to avoid is being misleading with your content. The best SEO practice is expertise, authority and trust (EAT).
Here are common technical SEO issues to avoid when running your website and SEO efforts:
Don’t:
- Apply Incorrect Keyword Targets – Using the wrong keywords will bring in the wrong users onto your website and make your SEO efforts moot.
- Ignore Local SEO – Local SEO is necessary to build a large keyword ranking profile for local law firms and private practices. Local SEO also counts for a large portion of overall search volume.
- Put Up Low Quality Content – The content on your website should be useful and unique. AI generated content should be avoided as it tends to lack unique insight and regenerates previously published content.
- Post Poor Quality Images – The images on your website should display correctly and should not be blurry, out of place, or be too small to properly use.
- Use Outdated NAP Information – Include your firm’s most up-to-date name, address, phone number, and other directory or contact information.
- Use a Non-Mobile Friendly Format – The website should be useable on both desktop and mobile devices. Ideally, the website should use a responsive design for mobile optimization.
- Running a Slow Website – Any webpage that takes more than a couple of seconds to load will crush your chances to be ranked for a given keyword. Load speed and performance are generally a large factor for organic rankings.
- Indexation Problems – Avoid using incorrect ‘no follow’ or ‘no index’ meta tags or blocking search engine crawl bots, creating crawl-bot black holes (crawl paths are replicated before deeper webpages are found and the crawl budget is used up), missing XML sitemap or HTML sitemaps.
Optimized URL Structure
URL structure can be used to influence SEO results. An organized URL structure can boost a website’s SEO rankings because they are easier for search engines to crawl and for potential clients to navigate. Be sure to determine your URL structure before launching your website as changing a URL structure on ranking webpages can negatively impact the value of those keywords, even if you restructure the URLs correctly. Organize your content in folders on the backend with titles that match the URL structure and breadcrumbs displayed on the webpages themselves.
A good URL structure is comprehendible not only to computers, but also to human users. Think about your URLs as an extension of your marketing. A string of random letters and numbers is difficult to remember, a headache to type out, and therefore a poor URL structure. On contrast, a good URL can serve to not only improve SEO output, but to reinforce your firm’s identity in the minds of potential clients.
For example:
⦁ Bad URL – lawfirm.com/tyhd93025ndks6.html
⦁ Good URL – lawfirm.com/family-law/child-custody.html
If you have a webpage that focuses on your office’s location, it is also good practice to include that location in your URL. This will not only help visitors find your physical location, it will also help you compete in local rankings.
For example: www.lawfirm.com/offices/city
On the other hand, non-optimized URL structures can lead to a host of technical problems from eating up a websites crawl budget to webpages never being indexed by the search engines.
Navigation & Hierarchical Webpage Structures
Website content should be intuitive for visitors to understand and navigate. A good user experience satisfies the user’s intent and won’t cause them to leave the website (bounce rate). Many jurisdictions mandate that a table of contents or a table of authorities be included in a brief if it exceeds certain page limits. Such tables help readers find the information they are looking for quickly. An organized website will have similar tools to help their users move around and find relevant information quickly.
SEO best practices include:
- Top-level navigation – Navigation refers to how easy it is for a user to move around your website. A website that is easy to use and find information on will rank highly in SEO results. If users cannot find what they are looking for, they may leave your website and may not return.
- Breadcrumbs – Breadcrumbs are navigation tools typically at the top of a webpage. Breadcrumbs will show exactly where a user is and how they got there. For example, the breadcrumb for an individual attorney might read: “Home > Office > Lawyer Name
- Internal links – Internal links are the links on a webpage and throughout a website that connect various webpages within the same website to each other. The home page for a law firm may have internal links that go to a staff member page and the staff member page may have links to each attorney’s and paralegal’s biographies. The staff member page and biographies should have internal links that go back to the home page or other pages on the website.
- HTML Sitemap – A HTML sitemap is a list of every page on your website intended to make navigating the website easy for users. Most HTML sitemaps can be found at the bottom of a webpage. Think of HTML sitemaps as the table of contents for your website, a tool that allows users to find exactly what they’re looking for without having to go through dozens of webpages to find it.
The purpose of a website is to deliver a good user experience that satisfies the user’s intent. If users are back-tracking or leaving your website (bounce rate), then your website is not meeting its most basic purpose and should be modified or even redesigned.
Link Equity, Internal Links and External Linking
Webpage links are another vital piece of on-page SEO optimization. Internal links, external links, and link equity contribute heavily to organic webpage rankings. Internal links are links that connect to internal webpages within your own website. Internal links are important as they distribute link equity within the website.
Eternal links are links that connect to external websites that are not part of your website. Linking to authoritative and trustworthy sources that can expand upon the information you present helps to build your own EAT profile within the industry.
Link equity is about the content of your links. Every website has a backlink profile and link equity is relevant to the size and weight of their backlink profile. The more links from authoritative domains a law firm website has, the stronger their backlink profile and the more link equity there is. Link equity is distributed through internal and external links. Ideally, link equity should be distributed in a way that mimics site structure (internal linking best practices) and benefits individual SEO campaigns for targeted keywords.
For example, adding internal links pointed to additional support (cross-linking or otherwise) will help the target keyword rankings by passing link equity.
Load Performance
Load speed, or load performance, is essential for SEO efforts. If search engines, and users, cannot use your website, then your website is not functional. Have you ever had a brief due but had a difficult time uploading it online for e-filing? If you felt frustrated by how slowly the website loaded, you may wish to avoid inflicting the same experience on people who may be your future clients.
You can measure load speed by using the Google Lighthouse Audit tool through web.dev/measure/ or by downloading the Chrome plugin and running it through the Chrome browser. The tool will return a report and help to eliminate all load performance issues. Optimal scores reach 50 at a minimum though 100 is ideal.
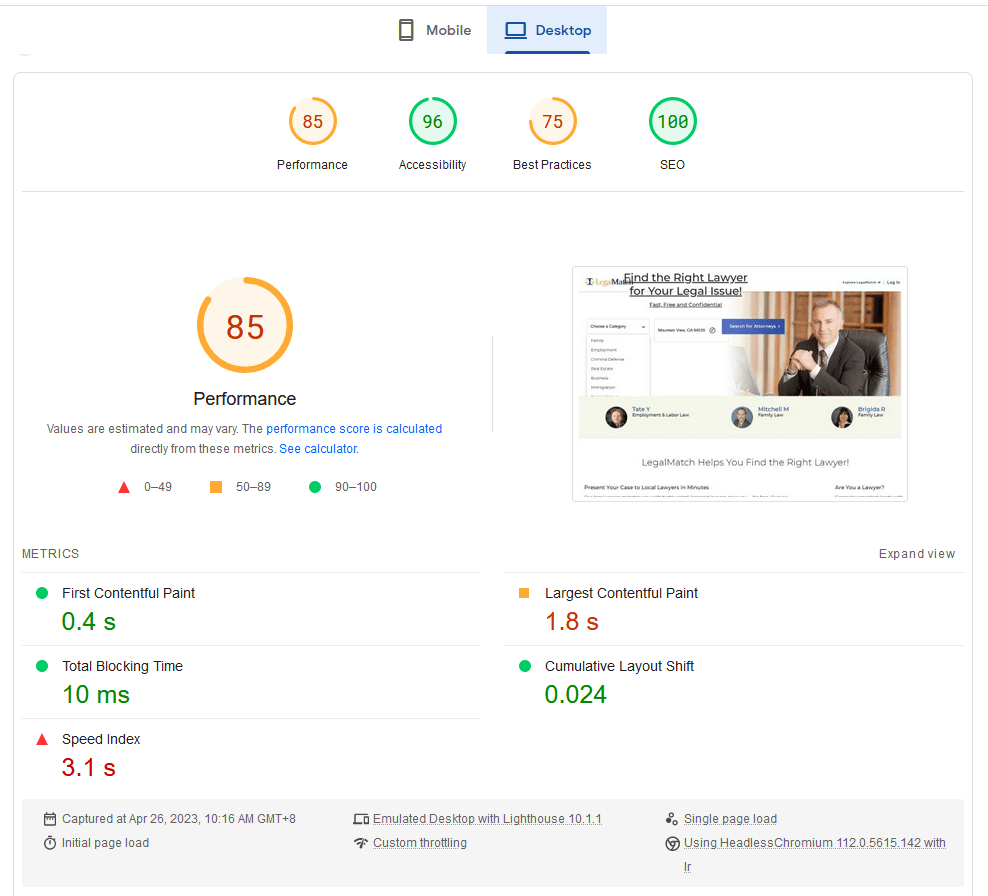
The web pages with the highest conversion rates have a load time between 0 and 2 seconds. Top recommendations to improve load performance include:
- Compression – You should use a compression system to reduce the file size of CSS, HTML, and Javascript files.
- Optimized Images – Use images that do not need to be resized for the webpage. CSS sprites can also be used to optimize templates and minimize the number of HTTP requests needed to load a webpage.
- Redirects – Eliminate any redirects from your webpage that are not necessary.
- Minification – CSS, Javascript, HTML and other webpage elements may not be needed and only weight down the load speed of your website. You should remove any webpage elements that are not necessary for your website to run.
- Rending-Blocking Javascript – The more scripts that can be removed or restructured (re-ordered or otherwise) on a webpage, the less time it will take for the browser to render the webpage.
- Server Response Time – The better your hosting is, the better your website will perform, ideally it should be beneath 200ms. Optimizing the amount of traffic relative to the amount of resources you need to facilitate that traffic is the best approach. Includes memory, database queries, or any other identified bottlenecks.
- Content Distribution Networks (CND) – You can use a CDN to improve the load speed that your webpage content can be served. Good CDNs will have data centers near areas that received large amounts of web traffic and are likely closer than your hosting server.
Also, you can use GTMetrix.com to get a more specific idea of which webpage elements are weighing your load speed down. You can run your webpage through the tool and select the Waterfall tab. You can view the resources used to load the webpage and which ones take the longest to load (which are your bottlenecks to resolve).
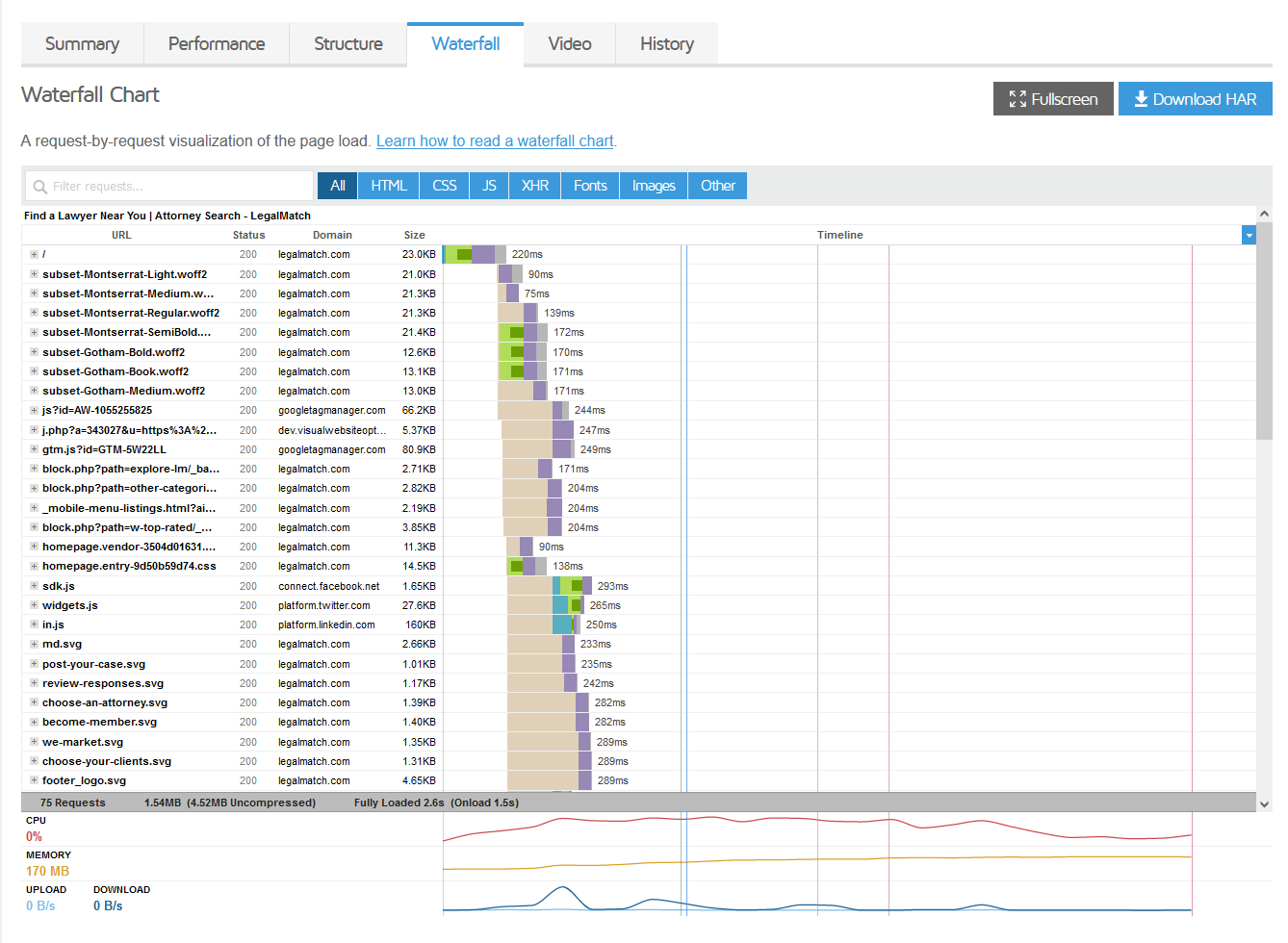
Many of the items to resolve load speed may require a front-end, back-end, or full-stack developer to resolve thoroughly.
Next Steps
The online visibility of your law firm depends on successful and continued on-page SEO strategies around keyword targeting, navigation, content quality, load speed, mobile-device compatibility and more. Which translates into a significant and ongoing investment of time, money, and research so you can adapt to ever-changing algorithms and user behaviors.
LegalMatch is here to help you simplify this process. As the leading platform for attorney-client matching, we let you leverage the benefits of large-scale online marketing efforts. When you become a LegalMatch member attorney, we send you a steady stream of potential clients. Instead of becoming a marketing expert, you can just focus on delivering quality legal services to those case leads.
To learn how other LegalMatch member attorneys have benefited from our services, read these success stories. And if you’re ready to view cases in your practice area and location, sign up for a free attorney guest pass.

